Highly sensitive and selective fluorescence detection of Hg(ii) ions based on R-phycoerythrin from Porphyra yezoensis
Abstract
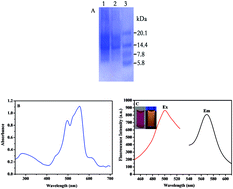
R-Phycoerythrin (R-PE) is a kind of natural fluorescent protein from marine Porphyra yezoensis. A highly sensitive and selective fluorimetric method has been developed to detect Hg2+ ions utilizing R-PE as a fluorescent probe. R-PE could respond selectively to Hg2+ ions among a series of metal ions. The reaction mechanism was investigated through UV-vis, fluorescence microscope imaging and fluorescence measurements. It was demonstrated that the interaction between the R-PE fluorescent probe and Hg2+ ions would cause fluorescence quenching. Besides, there was a linear relationship between R-PE fluorescence intensities and Hg2+ concentrations. A novel method was thus explored to detect Hg2+ ions with high sensitivity, selectivity, and a broad linear range of 0.0010–25.0 μM, which could allow for Hg2+ ions down to 0.0130 μM with a relative standard deviation of about 1.60%. Additionally, the method was successfully applied to detect Hg2+ ions in diverse water samples, showing the appropriate rates of recovery between 92.0% and 108.0%. This highly sensitive and selective natural green fluorescent probe of R-PE should have huge potential applications for detecting Hg2+ ions in diverse environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...