Optical-quality controllable wet-chemical doping of graphene through a uniform, transparent and low-roughness F4-TCNQ/MEK layer†
Abstract
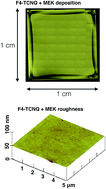
Controllable chemical doping of graphene has already proven very useful for electronic applications, but when turning to optical and photonic applications, the additional requirement of having both a high transparency and a low surface roughness has, to our knowledge, not yet been fulfilled by any chemical dopant system reported so far. In this work, a new method that meets for the first time this optical-quality requirement while also providing efficient, controllable doping is presented. The method relies on F4-TCNQ dissolved in methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) yielding a uniform deposition after spin coating because of an extraordinary charge transfer interaction between the F4-TCNQ and MEK molecules. The formed F4-TCNQ/MEK layer exhibits a very high surface quality and optical transparency over the visible-infrared wavelength range between 550 and 1900 nm. By varying the dopant concentration of F4-TCNQ from 2.5 to 40 mg ml−1 MEK, the doping effect can be controlled between Δn = +5.73 × 1012 cm−2 and +1.09 × 1013 cm−2 for initially strongly p-type hydrogen-intercalated graphene grown on 6H-silicon-carbide substrates, and between Δn = +5.56 × 1012 cm−2 and +1.04 × 1013 cm−2 for initially weakly p-type graphene transferred on silicon samples. This is the first time that truly optical-quality chemical doping of graphene is demonstrated, and the obtained doping values exceed those reported before for F4-TCNQ-based graphene doping by as much as 50%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...