Synthesis, characterization of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon spheres and adsorption performance
Abstract
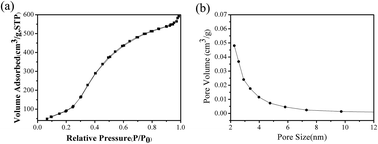
Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon spheres (NMCS) were prepared by a nanocasting route using benzoxazine resins as the precursor of nitrogen and carbon, and ordered mesoporous silica spheres as the hard template to remove methyl orange (MO) dye in aqueous solution. The prepared NMCS were respectively characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, nitrogen sorption, X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive spectrometry, elemental analysis, thermal gravimetric analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy technologies. The characterization results show that NMCS are amorphous spherical nanoparticles with worm-like mesoporous channels, the specific surface area, pore volume and nitrogen contents were 634 m2 g−1, 0.91 cm3 g−1 and 3.50 (wt%), respectively. MO adsorption on NMCS was well fitted with the Langmuir adsorption isotherm and monolayer maximum adsorption capacity was up to 352.1 mg g−1 at 318 K, it was suggested that NMCS have excellent adsorption capacity for methyl orange. MO adsorption kinetics was found to follow the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the intra-particle diffusion model indicates that the rate-controlling step of adsorption was determined simultaneously by external mass transfer and intra-particle diffusion. The thermodynamic parameters indicated MO adsorption was a spontaneous, endothermic and feasible process. The free energy change was −27.79 kJ mol−1, −29.07 kJ mol−1 and −30.32 kJ mol−1 at 298 K, 308 K and 318 K, and the enthalpy and entropy change was 9.835 kJ mol−1 and 126.3 J (mol−1 K−1). Moreover, good regeneration properties and long life were observed for NMCS through the desorption experiments. MO adsorption should be mainly controlled by electrostatic attraction mechanism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...