Insight into structural and π–magnesium bonding characteristics of the X2Mg⋯Y (X = H, F; Y = C2H2, C2H4 and C6H6) complexes†
Abstract
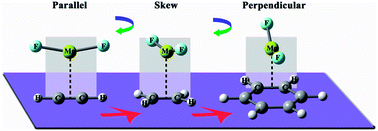
Quantum chemical calculations have been performed to study the nature of interaction of complexes formed by MgX2 (X = H, F) molecules with acetylene, ethylene, and benzene, respectively. Results indicate that nonbonded interactions, namely π–magnesium bonds, contribute to the stability of the resulting dimers. An intriguing structural evolution has been found for the complexes with different π electron donors. Upon complexation, both the Mg–X and C–C bonds lengthened, accompanied by redshifted X–Mg–X and C–C stretching vibrations. NBO analysis reveals that the main charge-transfer from the conjugated molecules to MgX2 is from the πCC bonding orbital to the empty lone pair orbital of Mg. Energy decomposition analysis indicates that the stability of the topic complexes mainly comes from the attractive electrostatic interaction and polarization, similar to the case of π–beryllium bonds. When compared with other nonbonded interactions, it is found that π–magnesium bonds are stronger than π–lithium and π–sodium bonds. Especially, they are comparable in strength to π–beryllium bonds with MgF2 playing the role of Lewis acid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...