Probing the electrochemical behavior of {111} and {110} faceted hollow Cu2O microspheres for lithium storage†
Abstract
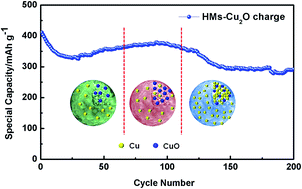
Transition metal oxides with exposed highly active facets have become of increasing interest as anode materials for lithium ion batteries, because more dangling atoms exposed at the active surface facilitate the reaction between the transition metal oxides and lithium. In this work, we probed the electrochemical behavior of hollow Cu2O microspheres with {111} and {110} active facets on the polyhedron surface as anodes for lithium storage. Compared to commercial Cu2O nanoparticles, hollow Cu2O microspheres with {111} and {110} active facets show a rising specific capacity at 30 cycles which then decreases after 110 cycles during the cycling process. Via advanced electron microscopy characterization, we reveal that this phenomenon can be attributed to the highly active {111} and {110} facets with dangling “Cu” atoms facilitating the conversion reaction of Cu2O and Li, where part of the Cu2O is oxidized to CuO during the charging process. However, as the reaction proceeds, more and more formed Cu nanoparticles cannot be converted to Cu2O or CuO. This leads to a decrease of the specific capacity. We believe that our study here sheds some light on the progress of the electrochemical behavior of transition metal oxides with respect to their increased specific capacity and the subsequent decrease via a conversion reaction mechanism. These results will be helpful to optimize the design of transition metal oxide micro/nanostructures for high performance lithium storage.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...