Phenylsulfonic acid functionalized carbon quantum dots based biosensor for acetylcholinesterase activity monitoring and inhibitor screening†
Abstract
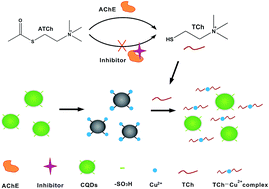
Phenylsulfonic acid functionalized carbon quantum dots (PSA-CQDs) were prepared and used to construct a convenient and reliable fluorometric biosensor for acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and inhibitor screening. Effective static quenching process occurred owing to the formation of nonfluorescent complex when copper(II) ions were added to PSA-CQDs, which results in its fluorescence quenching due to strong coordination of copper ions to sulfonic groups of PSA-CQDs. As a result, the fluorometric assay for AChE was established based on the stronger affinity between copper and thiocholine hydrolyzed from acetylthiocholine under the hydrolysis of AChE which can induce fluorescence recovery. Meanwhile, the inhibition effect of tacrine to AChE was assessed because its effective inhibition effect to AChE leads to the prevention of hydrolysis of acetylthiocholine and the following occurrence of PET process which causes the quenching of fluorescence. This detection method is convenient and efficient, which has high sensitivity with detection limit as low as 2.6 U L−1 and a broad linear scope ranging from 3.8 to 80.0 U L−1. This work proposed a competitive assay strategy among the sulfonic acid modified probe, copper cation and thiocholine to quantify AChE activity using functional carbon quantum dots, and can be utilized to design detection methods for other thiol-containing targets of interest.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...