Inactivation of E. coli bacteria ingested by Limnoithona sinensis and Daphnia magna using chloramines
Abstract
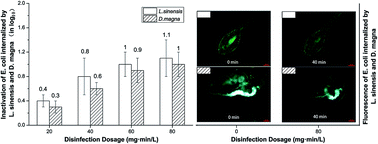
Zooplankton may harbor bacteria and protect them from disinfection inactivation while treating drinking water. This has rarely been quantified in research studies using chloramines to inactivate Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria ingested by zooplankton. In this study, chloramines (2 mg L−1) were used to inactivate the internalized E. coli bacteria ingested by zooplankton (Limnoithona sinensis and Daphnia magna). The results showed that both Limnoithona sinensis and Daphnia magna could protect the internalized E. coli against chloramination and the latter could provide stronger protection. The transfer of chloramines, from the bulk water into the guts of zooplankton by ingestion, was inhibited when chloramines were used as disinfectants, reaching the E. coli bacteria in the digestive tract of zooplankton mainly via penetration. The amount of internalized E. coli killed by chloramines increased with the increase in Ct values, whereas the quantity of chloramines really affecting the internalized bacteria decreased. It was found that 1.1 log10 reduction of the internalized E. coli in L. sinensis and 1.0 log10 in D. magna were obtained at a Ct value of 80 mg min L−1, with less than 40% of the applied disinfection reaching the ingested bacteria. The pH value had an obvious impact on the inactivation effect, whereas the temperature had little influence.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...