Optimizing the efficiency of antioxidants in emulsions by lipophilization: tuning interfacial concentrations
Abstract
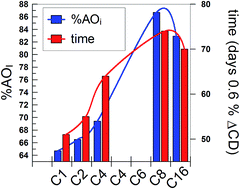
Optimization of the efficiency of antioxidants, AOs, in lipid-based emulsions via chemical modifications of their reactive moieties is not always possible because of the inherent experimental difficulties and because of the regulatory status of AOs. Esterification of hydrophilic AOs may be a practical, convenient, alternative approach. Here we employed a series of caffeic acid derivatives bearing the same reactive moiety but of different hydrophobicity (alkyl chain lengths of 1 to 16 carbon atoms) to investigate the effects of hydrophobicity on the oxidative stability of stripped corn oil-in-water emulsions. AO efficiency was determined by monitoring the production of primary oxidation products (conjugated dienes) with time and a non-linear, parabolic-like, variation of their efficiency with the number of C atoms in their alkyl chain, with a maximum at the C8 derivative, found. To rationalize the results, we also determined the distribution of the AOs between the oil, interfacial and aqueous regions of the same emulsions by employing a recently developed kinetic method that provides the partition constants of the AO between the oil–interfacial, PIO, and water–interfacial, PIW, regions of the intact emulsions. Values of both PIO and PIW range between 180–2000, suggesting that the transfer of the AOs to the interfacial region is spontaneous. The results indicate that the variations of both the percentage of AO in the interfacial region, % AOI, of the emulsions and the AO efficiency with the number of C atoms in the AO alkyl chain parallel each other with a maxima at the C8 derivative. The results illustrate an effective and convenient way to control lipid oxidation by modulation of the hydrophobicity (HLB) of the AOs. An increase in the alkyl chain length of the AOs promote their incorporation into the interfacial region of emulsions but only up to a critical chain length, after which a further increase makes their efficiency decrease as a consequence of the decrease in their % AOI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...