Magnetic organic–inorganic nanocomposite with ultrathin imprinted polymers via an in situ surface-initiated approach for specific separation of chloramphenicol†
Abstract
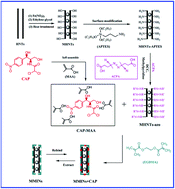
An approach for preparing novel magnetic organic–inorganic nanocomposites with ultrathin imprinted polymers was reported, via an in situ surface-initiated grafting technique from magnetic halloysite nanotubes (MHNTs). These magnetic surface molecularly imprinted nanomaterials (MMINs) were used as advanced nanoadsorbents for specific separation of chloramphenicol (CAP) from water. The thickness of the imprinted polymer was well controlled by adjusting the addition amount and solvent volume. The optimal conditions for adsorption performance of MMINs included using methacrylic acid (MAA) as a functional monomer, and a ratio of MMA : CAP was 1 : 6 with an acetonitrile volume of 15 mL, which showed an ultrathin imprinted nanoshell of 8.5 nm. The ultrathin imprinted nanoshell made all the imprinted cavities efficient and easily accessible. Thus, MMINs exhibited fast adsorption kinetics with equilibrium time of about 20 min. The adsorption equilibrium and kinetic data could be well described by the Freundlich isotherm model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model, respectively. MMINs had an excellent specific adsorption capacity of CAP from water compared with other antibiotics. Also, MMINs exhibited excellent regeneration properties and stability, as well as good magnetic separation, providing the possibility for practical antibiotic wastewater treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...