Cisplatin and doxorubicin dual-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery†
Abstract
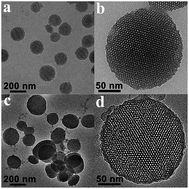
Multicomponent therapeutic platforms have been proposed to minimize dosage of each drug and reduce toxicity, leading to achieving a synergistic effect and maximizing therapeutic efficacy. In this work, a novel dual drug co-delivery system based on poly(acrylic acid) modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles (PAA-MSNs) for the combination of doxorubicin (DOX) and cisplatin (Pt@PAA-MSNDOX) was designed and synthesized. The cisplatin was conjugated with carboxyl groups to form pH-responsive crosslinking shells after the encapsulation of DOX into the mesopores of MSNs. The obtained shell cross-linking nanocomposites were confirmed by various spectroscopic methods. The drug release behaviour of the dual drug loaded nanocomposites was pH sensitive. As a result, 70.0% of Pt(II) and 79.9% of DOX were released within 144 h at pH 5.5 with 0.9% NaCl, while only 15.9% of Pt(II) and 25.3% of DOX was released at pH 7.4. Confocal fluorescence microscopy revealed that Pt@PAA-MSNDOX nanocomposites effectively delivered and released DOX to the nuclei of HeLa (human cervical carcinoma) cells. An in vitro cell assay demonstrated the high biocompatibility of PAA-MSN and increased cytotoxicity of Pt@PAA-MSNDOX nanocomposites in both HeLa and A357 (human melanoma cells) tumor cells with respect to free single drug or single drug loaded nanoparticles at the same dosage. This unique drug co-delivery system using an anticancer drug as a cross-linking linkage suggests a promising application in multi-drug delivery for combination cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...