Ecological insights into low-level antibiotics interfered biofilms of Synechococcus elongatus†
Abstract
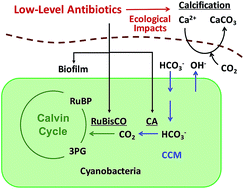
The interactions between antibiotics and microorganisms have attracted considerable interests. As reported, low-level concentrations of antibiotics have been detected in various environments. Although many studies reported the inducing effects of antibiotics on biofilms, few research discussed their impacts on the ecological functions of microorganisms with biogeochemical importance. In this study, we investigated the effects of low-levels of kanamycin on the biofilm formation of Synechococcus elongatus as a proof of principle study. The results indicated that the biofilms of S. elongatus would be promoted in the presence of kanamycin, and the related photosynthesis-mediated calcification, a fundamental bio-machinery contributing to the local and global carbon cycle, will probably be enhanced as well. We believe this study would offer new information to evaluate the environmental risks of antibiotics and inspire more investigations on the ecological impacts of emerging pollutants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...