Effect of superparamagnetic nanoparticles on the physicochemical properties of nano hydroxyapatite for groundwater treatment: adsorption mechanism of Fe(ii) and Mn(ii)
Abstract
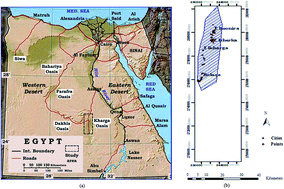
Magnetic hydroxyapatite (MHAP) was found to be an ideal adsorbent for Fe(II) and Mn(II) in ground water from the El-Kharga Oasis in Egypt. The formation of surface iron phases strongly enhances the adsorption capacity of hydroxyapatite-based materials for Fe(II) and Mn(II) ions. Batch sorption studies were implemented to investigate the effect of parameters such as the contact time, dosage of MHAP, pH, agitation speed and temperature on the adsorption process. The results revealed that a good correlation with experimental data was described well by the Langmuir model and the pseudo-second-order model, which explained well the mechanism of adsorption. It was found that the adsorption process was achieved mainly via surface complexation and ion exchange. We found various dominating adsorption mechanisms by changing the initial solution pH. The thermodynamic parameters suggested that the adsorption of Fe(II) and Mn(II) were a non-spontaneous endothermic process. Moreover, the adsorption capacities were affected by several parameters such as contact time, adsorbent dosage, and initial pH. After sorption, the MHAP composites could be effectively and easily separated from aqueous solutions by an external magnet. The results revealed that MHAP had the potential to become a promising material for in situ heavy metal-contaminating groundwater remediation in large scale.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...