Identification of novel cathepsin K inhibitors using ligand-based virtual screening and structure-based docking†
Abstract
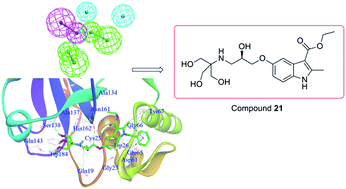
A combination of virtual screening and biological testing was used to identify novel cathepsin K (Cat K) inhibitors. A ligand-based pharmacophore model with five features was constructed and used for the virtual screening, which was followed by structure-based docking. Compounds were selected for biological testing based on fit values in the pharmacophore matching, structural diversity, binding pocket location and docking score in the screening. Four (compounds 3, 4, 5 and 21) out of twenty-two initial in silico hit compounds showed promising Cat K inhibition with IC50 values of 19.21, 24.83, 21.43 and 17.73 μM, respectively. Three compounds also showed anti-proliferative activity against one or more cancer cell lines with micromolar IC50 values. Compound 21 was the most promising hit with IC50 values of 28.25, 16.35 and 5.05 μM against HCT116, MCF7 and 143B cancer cell lines, respectively. This pioneering work has identified novel Cat K inhibitors using virtual screening in combination with pharmacophore modeling and docking approaches. Compound 21 could be used as a scaffold for the development of novel Cat K inhibitors with anti-proliferative activities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...