Paris saponin I inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis through down-regulating AKT activity in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells and inhibiting ERK expression in human small-cell lung cancer cells†
Abstract
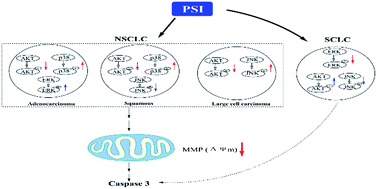
Paris Saponin I (PSI), a steroidal saponin derivative extracted from a traditional Chinese herbal Paris polyphylla, has shown cytotoxic effects on several tumor cell lines. However, the mechanisms of its antitumor activity especially for lung cancers remain to be elucidated. In this present investigation, we continue to explore the efficacy and mechanisms underlying the cytotoxic effects of PSI in lung cancer cell lines. Three non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells (H1299, H520, H460) and one small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cell (H446) were treated with PSI for the first time. PSI significantly induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and mitochondrial-related apoptosis NSCLC cells but not SCLC cells. Additionally, PSI reduced phosphorylation of AKT in NSCLC and ERK in SCLC in general. Interestingly, we observed that PSI influenced different signaling pathways among the four kinds of lung cancer cells. After PSI treatment, p38 MAPK and ERK activation were observed in H1299, while p38 MAPK increased and JNK decreased in H520. On the contrary, we found JNK activation in H460 cells with PSI. However, PSI upregulated the AKT activity and inhibited the JNK expression in H446 cells. The results indicate that PSI exhibits the cytotoxicity in different pathways depending on the cancer types.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...