Fabrication of a composite of nanocrystalline carbonated hydroxyapatite (cHAP) with polylactic acid (PLA) and its surface topographical structuring with direct laser writing (DLW)†
Abstract
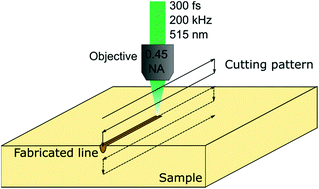
The fabrication of a polylactic acid (PLA)–carbonated hydroxyapatite (cHAP) composite material from synthesised phase pure nano-cHAP and melted PLA by mechanical mixing at 220–235 °C has been developed in this study. First, we report the cHAP nanocrystalline powder synthesis via a wet chemistry approach from calcium acetate and ammonium hydrogen phosphate precursors together with a crosslinking agent of polyethylene glycol, poly(vinyl alcohol) and triethanolamine. The calcination temperature of the cHAP was evaluated by thermal analysis, mass spectrometry and dilatometry measurements to be 680 °C. The X-ray diffraction showed that powders calcined at 680 °C are phase pure and crystalline. The formation of A- and B-type substituted cHAP was revealed by FT-IR spectroscopy. Further we present the preparation of the PLA–cHAP composite and surface microstructuring using the direct laser writing (DLW) technique. The depth of produced grooves was estimated to be around 25 μm and the width was 5–20 μm, the latter is laser power, translation velocity, and composition dependent. Scanning electron microscopy indicates that most evenly cut grooves with nanoparticles of cHAP homogeneously exposed to the surface were obtained for 5 and 10 wt% cHAP–PLA composites. The improvement of elastic modulus compared to the neat PLA was due to the cHAP, and the best results were obtained for composites loaded with 5% and 10% inorganic filler.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...