Uptake of Fe(iii), Ag(i), Ni(ii) and Cu(ii) by salicylic acid-type chelating resin prepared via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization
Abstract
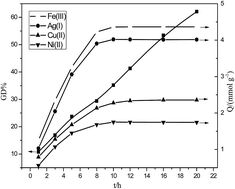
With chloromethylated polystyrene resin being the base material, a new type of salicylic acid-type chelating resin with high capacity was prepared by grafting glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) on the surface of the resin via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization and followed by the derivatization with 5-aminosalicylic acid. Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were used to characterize the surface composition of the resin. It was found that the grafting degree of GMA increased linearly with the extension of ATRP time and GMA concentration. The maximum adsorption capacities of the resin were up to 4.23 mmol g−1 for Fe(III), 4.02 mmol g−1 for Ag(I), 2.36 mmol g−1 for Ni(II) and 1.75 mmol g−1 for Cu(II) at pH 4.0, respectively. The adsorption kinetics of the four metal ions conform to the model of pseudo second-order kinetics, and adsorption equilibria were better characterized by the Langmuir equation. Thermodynamic parameters were calculated to understand the nature of the adsorption process. The resin possesses excellent desorption rate and reusability. All these results indicate that the resin could be potentially applied to the efficient removal of heavy metal ions from waste water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...