Influence of surface chemistry on the ionic conductivity of vertically aligned carbon nanotube composite membranes
Abstract
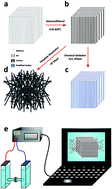
The nano-sized solid state pores and channels that mimic nature-based systems have attracted great interest due their potential applications for molecular separation, sensing, drug delivery, and energy conversion. In this study, in order to gain more knowledge on the ion and molecular transport inside nanopores, we examined how the surface conduction and electrochemical properties of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) composite membranes produced by a template-assisted catalyst-free chemical vapour deposition (CVD) process using nanoporous anodic alumina membranes (NAAMs) as a template can be tuned readily by chemical modification of their inner surface for various applications. The inner graphitic surface of the resulting CNTs was modified chemically through wet oxidation process using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as the oxidant agent to introduce oxygen-containing groups, mainly carboxyl groups. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) revealed significant changes in surface conduction measured by impedance and conductance of CNTs as a result of the selective chemical modification of their inner wall surfaces. These results show that this approach makes it possible to tune the surface conductivity and interfacial properties of vertically aligned arrays of CNTs with precision, using a simple oxidation process. Therefore, this method can be used to produce CNTs composite membranes with precisely controlled electrochemical properties and conductivity related to potential applications of advanced electrically driven and bioinspired separation devices for water desalination and separation of biological molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...