Magnetic NiO nanoparticles confined within open ends MWCNTs: a novel and highly active catalyst for hydrogenation and synthesis of imines†
Abstract
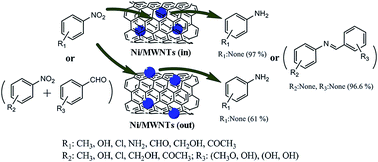
A new nanocatalyst has been synthesized by confining magnetic nickel nanoparticles within carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and characterized by XRD, TEM, Raman and VSM. The character of the nanocatalyst passivated with a gas mixture was that it can be stored safely in air below 150 °C and needs no activation prior to use. In the catalytic test, a nickel oxide nanocatalyst confined inside the Multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanochannels (NiO/MWCNTs-in) was found to be a highly efficient and reusable catalyst for the reduction of various aromatic nitro compounds to various aromatic amines, the conversion and selectivity of which were almost up to 100% and exceed 80%. The prominent merit of the catalyst is that the overall formation rate of product inside the nanotubes exceeds that outside. Moreover, it is inexpensive, and could be prepared and scaled up easily. Besides, it can be simply separated from the reaction mixtures by an external magnetic field As a result of the possible confinement effect of CNTs, the employment of the CNTs channels as nanoreactors for catalysis may provide opportunities for the development of new heterogeneous catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...