Performance and antifouling enhancement of polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes incorporated with highly hydrophilic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles
Abstract
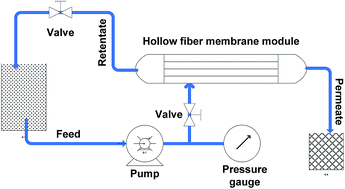
Membrane fouling is one of the main drawbacks in water purification applications. In this regard, the present study is an attempt to investigate the effects of hydrophilic HAp nanoparticle addition on permeability and antifouling behavior of hydrophobic PES hollow fiber membranes. Hydroxyapatite (HAp) nanoparticles were self-synthesized via a chemical precipitation method and were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). HAp nanoparticles were incorporated into a polyethersulfone (PES) hollow fiber membrane along with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a pore former. The hollow fiber membrane morphology and surface topography were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM). The hydrophilicity of the membranes was investigated via contact angle measurements. According to the results, the addition of 2 wt% HAp into the doping solution could increase the water permeation from 67 up to 148.7 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. The results confirmed that hydrophilicity, porosity, pore size and rejection properties of the membranes were dependent on HAp concentration. Flux recovery of the hollow fiber membranes after cleaning with deionized water was improved considerably by increasing nanoparticle concentration, indicating the enhancement of membrane anti-fouling characteristics upon the addition of HAp nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...