A rheological study of reverse vesicles formed by oleic acid and diethylenetriamine in cyclohexane†
Abstract
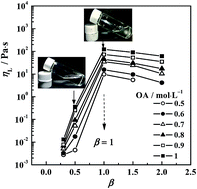
A reverse aggregate system composed of oleic acid and diethylenetriamine in cyclohexane has been studied. Small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements and polarising microscopy (POM) observations suggested the formation of reverse vesicles. FT-IR measurements showed simple attraction between DETA and OA, which increased the size of the head of the forming unit and resulted in reverse vesicle formation. Therefore, the viscosity of solutions depended on the mole ratios of DETA to OA,β, and reached a maximum of 122 Pa s at β = 1 for 1 mol L−1 OA. Dynamic oscillatory sweeps were carried out for this system of equi-mole mixed OA (1 mol L−1) and DETA. Strong elasticity was observed, where the elastic modulus (G′) always dominated over the viscous modulus (G′′) over the range of examined frequencies. The elastic plateau modulus G′P was 127.4 Pa and G′P was found to decrease exponentially with temperature. Strain sweeps exhibited a strain-softening response at high strains. The effect of trace amounts of water was also examined for equi-mole mixed OA (1 mol L−1) and DETA, where the reverse vesicles remained. The water was found to improve the association of DETA with OA and increase the visco-elasticity of the solution. The maximum viscosity was as high as 6005 Pa s at W0 = 6, and G′P also reached 530 Pa. The solution became gelatinous in appearance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...