Improving the mechanical stability of proton conducting SPEEK membranes by in situ precipitation of zirconium phosphate phenylphosphonates
Abstract
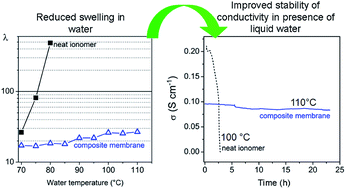
The formation of layered zirconium phosphate phenylphosphonates, Zr(O3POH)2−x(O3PC6H5)x (hereafter ZP(PP)x, with x in the range 0–2.0) from precursor solutions of zirconyl propionate, phosphoric and/or phenylphosphonic acids was studied by using NMP as solvent. On the basis of this investigation, composite membranes made of a SPEEK matrix (EW = 625, hereafter FUM) filled with ZP(PP)x, with x = 0, 0.72 and 2.0 and filler loading up to 36 wt%, were prepared by casting mixtures of the precursor solution and a FUM dispersion in NMP. All the composite membranes exhibited lower swelling in water than FUM up to 110 °C, and, among them, the membrane with 32 wt% ZP(PP)0.72 (hereafter FUM/ZP(PP)0.72-32) showed the lowest water uptake and the highest Young's modulus, with a proportional increase up to 60% with respect to FUM, at 70 °C and 80% relative humidity (RH). At 80 °C, the proton conductivity of all the composites decreased with increasing filler loading, and FUM/ZP(PP)0.72-32 was less conductive than FUM by a factor of ∼5, both at 50% and 95% RH. However, differently from FUM, the conductivity of FUM/ZP(PP)0.72-32 turned to be stable over time even at 110 °C in the presence of liquid water, being around 0.1 S cm−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...