Bimetallic Ag–Cu alloy nanoparticles as a highly active catalyst for the enamination of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds†
Abstract
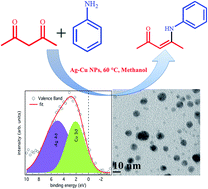
Bimetallic nanoparticles, particularly those based on copper, have recently attracted a great deal of attention for the development of low cost and highly active catalysts due to the synergistic interaction between individual metal components. In this work, bimetallic Ag–Cu alloy nanoparticles were explored as a highly active and reusable catalyst for the enamination of 1,3-dicarbonyls using diverse amines. The nanocatalysts were intensively characterized by ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy-energy-dispersive spectroscopy (HRTEM-EDS) and valence band and core level X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) to study the effect of the bimetallic structure and composition. In comparison to monometallic Ag and Cu nanoparticles, the alloyed Ag–Cu nanoparticles showed a high catalytic performance and the resultant catalytic activity was dependant on the Ag to Cu ratio. This enhanced catalytic activity should be related to the electronic interaction between Ag and Cu nanoparticles formed due to the intimate contact between them. Our study may serve as a foundation for designing efficient alloyed nanocatalysts for fine chemical synthesis via enamination reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...