Tuning the reaction rates of fluoride probes for detection in aqueous solution†
Abstract
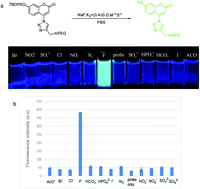
Fluoride detection in aqueous solution has drawn much attention. Most fluoride probes are based on the cleavage of a silyl group by fluoride for the generation of fluorescence. However, such a reaction is generally slow in aqueous solution. Herein we successfully demonstrate the concept that increasing the hydrophilicity of a pendent group enhances the reactivity of a silyl-based probe for fluoride detection in aqueous solution. By applying this concept, we also developed a new probe with a pendent PEG unit (BW-F-204), which showed excellent fluoride sensing ability both in aqueous solution and in cell culture.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...