Well-defined degradable brush-coil block copolymers for intelligent release of insulin at physiological pH†
Abstract
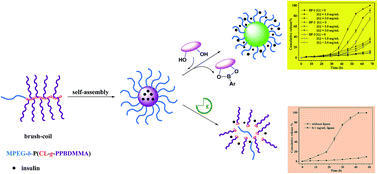
To achieve an intelligent glucose responsive insulin delivery system with reasonable glucose-sensitivity and minimal long-term side effects, a kind of degradable brush amphiphilic polymer was synthesized through grafting-from strategy of poly[(2-phenylborate esters-1,3-dioxane-5-ethyl) methylacrylate] (PPBDMMA) as a side chain via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and the poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) backbone fabricated by ring-opening polymerization of α-bromo-caprolactone (α-BrCL) monomers using monomethylpoly(ethylene glycol) (MPEG) as an initiator. The well-controlled structures of the resulting brush polymers were verified by 1H NMR and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) characterizations. These brush polymers MPEG-b-P(CL-g-PPBDMMA) were self-assembled to form polymeric micelles with a hydrophobic core composed of both glucose-responsive PPBDMMA and biodegradable hydrophobic PCL. These nanocarriers exhibited a very low insulin release at a glucose concentration of 1.0 mg mL−1 (normoglycemia) and a relatively rapid release at 3.0 mg mL−1 (hyperglycemia) at pH 7.4. The glucose-triggered on–off release of insulin at pH 7.4 with alternate 1.0 and 3.0 mg mL−1 glucose incubation further exhibited effective controllable insulin delivery in response to physiological glucose level fluctuation. The cell viability of all the nanoparticles investigated by the MTS assay was higher than 80%, indicating that these brush polymers had good cytocompatibility. The benign degradability of these nanocarriers in the presence of Novozym 435 was evidenced in this study. This type of nanocarrier may be a promising candidate for in vivo insulin delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...