Fabrication and origin of flame retarding glass fiber/bismaleimide resin composites with high thermal stability, good mechanical properties, and a low dielectric constant and loss for high frequency copper clad laminates†
Abstract
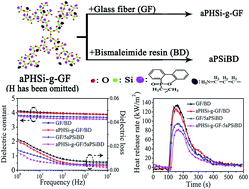
Higher frequency, higher speed and smaller dimensions have been the developing trends for electric information products, so the key and basic materials, glass fiber (GF)/polymer composites (GFRPs), for high frequency copper clad laminates (HFCCLs), should have better integrated performances, especially high flame retardancy, outstanding thermal stability, good mechanical properties, and low dielectric constant and loss. However, almost all GFRPs do not have high flame retardancy. In order to overcome the problem, a new hyperbranched polysiloxane (aPHSi) with both phosphaphenanthrene and amino groups was designed and synthesized, which was then grafted on GF to prepare a novel hybridized GF (aPHSi-g-GF), or used to modify bismaleimide/diallylbisphenol A (BD) with different loadings. To evaluate the effect of the modification for GF and BD, eight composites were prepared using GF or aPHSi-g-GF as reinforcement, and BD or aPHSi modified BD (aPSiBD) as the matrix. The results show that the aPHSi-g-GF/5aPSiBD composite, in which the ratio of aPHSi to BD is 5 : 100, has the highest flame retardancy, and it has a 64% higher limited oxygen index, 39.6% lower peak heat release rate (PHRR), 6 s longer time to ignition (TTI) and 12 s shorter time of flameout (TOF) than the GF/BD composite. Besides, modified composites have an 11.3–14.3 °C higher initial thermal degradation temperature, higher flexural strengths, and lower dielectric constant and loss. Matrix modification plays greater roles in reducing the PHRR, TOF, dielectric constant and loss as well as improving the thermal stability and mechanical properties; while the grafting of GF is more active in lengthening the TTI. These remarkable improvements indicate that modified composites can meet the harsh requirements for fabricating HFCCLs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...