Conductive hybrid carbon nanotube (CNT)–polythiophene coatings for innovative auditory neuron-multi-electrode array interfacing
Abstract
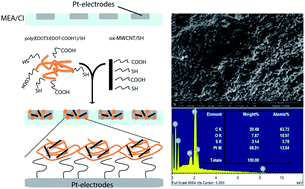
Cochlear implants (CIs) are neuroprosthetic devices that restore hearing in deaf patients. They consist of a linear electrode array surgically inserted into the scala tympani of the cochlea. In this position the array directly stimulates the spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs), bypassing lost or nonfunctioning sensory hair cells. In order to reduce the energy needed to stimulate the SGNs, we attempted to improve the conductivity of the CI electrodes by creating conductive nanocomposites. We assessed the functional modification of CI platinum (Pt) pads by using multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) either alone or in combination with a conductive polythiophene phase, to obtain conductive nanocomposites (NCs). A novel functional poly(EDOT3:EDOT-COOH1) copolymer was synthesized by liquid-phase oxidative polymerization (LPP) of both 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) and carboxylated EDOT (EDOT–COOH) monomers. Molar ratios of monomers EDOT3:EDOT-COOH1 were obtained and a poly(EDOT3:EDOT-COOH1) polymeric phase was further incorporated with oxidized MWCNTs (ox-MWCNTs) to obtain a homogeneous conductive NC phase. Immobilization of single components or NC onto Pt electrodes using cysteamine-based covalent modification has been achieved and characterized. Impedance spectroscopy of Pt-modified electrodes showed a reduced resistance at different frequencies for the specific NC consisting of poly(EDOT3:EDOT-COOH1)/SH/ox-MWCNTs/SH (1 : 1 wt%). Finally, we revealed the functional outcome of these nanostructured chemical modifications concerning the stimulation of SGN in vitro using multi-electrode arrays (MEAs). We aimed at reducing the energy needed to stimulate the SGNs and obtain an effective neuronal response. This has been observed for Pt electrodes modified with NC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...