Polyphenols from pinecones of Pinus koraiensis induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells through the activation of caspase in vitro
Abstract
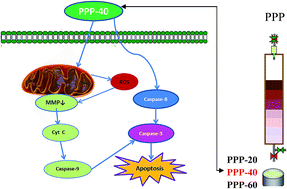
We had previously extracted and purified a polyphenol from P. koraiensis pinecone (PPP), and evaluated its antiproliferative activities against different cancer cells lines. In the present study, we further improved the purity of PPP through the gradient elution method by different concentrations of ethanol (20%, 40% and 60%), so as to study their antitumor effects. Then, the purity and the influence upon cell viability of the purified components from PPP (PPP-20, PPP-40 and PPP-60) were evaluated. The results showed that PPP-40 had the highest phenolic purity (57.25 ± 1.83%) and exhibited the strongest inhibition (EC50 0.21 ± 0.03 mg mL−1) against LOVO cells in a dose-dependent manner. Catechin and taxifolin, the main components of PPP-40, may contribute to its antitumor activity. Moreover, we further investigated the molecular mechanisms of the PPP-40-induced apoptosis. The DNA damage in LOVO cells was observed by PI staining and comet assay. Besides, the apoptosis rates were further detected by flow cytometry. Consequently, the data showed that PPP-40 could significantly disrupt the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), reduce the content of adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) and increase the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). All the results indicated the mitochondrial dysfunction was involved in the PPP-40-induced apoptosis. Meanwhile, the typical markers of apoptosis involving the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways were analyzed as well. This showed that PPP-40 could not only promote the intrinsic apoptosis by increasing the release of cytochrome c (cyt c) and activating caspase-9 and -3, but also induce extrinsic apoptosis by activating caspase-8.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...