The stability of magnetic chitosan beads in the adsorption of Cu2+†
Abstract
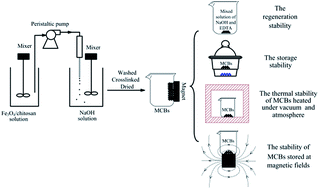
Magnetic chitosan beads (MCBs) synthesized through a common embedding method and crosslinked with glutaraldehyde were studied for the adsorption of Cu2+ in aqueous solution. MCBs were investigated by means of hysteresis curves, thermo-magnetization curves, TGA, FTIR and XRD. Kinetic, isothermal and thermodynamic studies were applied to investigate the adsorption of Cu2+ by the MCBs. The effects of the pH value and the coexisting ions on the adsorption of Cu2+ were explored. Subsequently, the stability of the MCBs including the adsorption capacity (Qe) and the saturated magnetization (Ms) stability was investigated under various conditions. Simultaneously, FTIR and XRD were utilized to further analyze the change in the MCBs in the stability studies. The results suggested that the MCBs showed good stability without a significant loss in Qe and Ms after regeneration from five sequential cycles. The MCBs presented excellent storage stability while stored in a drying vessel for ten months. For thermal stability, the Qe and Ms of the MCBs presented similar variations after being heated in the atmosphere and in a vacuum at different temperatures for 30 h. The Qe changed slightly after being heated at 50 and 100 °C, and decreased sharply at 150 and 200 °C. The magnetization was stable in the lower temperature range (50–150 °C) and increased slightly at 200 °C. Different magnetic fields had little effect on the stability of the MCBs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...