Discovery of serum metabolites for diagnosis of progression of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease using an optimized metabolomics method†
Abstract
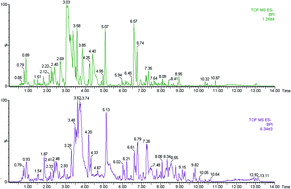
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is considered to represent early AD. Currently, there is a great need for sensitive tools to monitor the progression of MCI to AD. In this work, a nontargeted metabolomics approach was developed to examine metabolic differences in serum samples from the MCI subjects and the age-matched AD subjects. Based on principal component analysis, metabolic differences among AD and MCI subjects were identified. Nine metabolites in the serum of the AD subjects were significantly different from the MCI subjects. Two metabolites were selected as the candidate biomarkers and validated in separate and independent patient cohorts. The major contributors to the predictive model were upregulated sphinganine-1-phosphate and 7-ketocholesterol, which yielded satisfactory sensitivity, and specificity, indicating potential value for predicting the conversion of MCI to probable AD. The present study may provide a diagnosis tool to monitoring the progression of MCI to AD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...