Cleavage of carbon suboxide to give ketenylidene and carbyne ligands at a reactive tungsten site: a theoretical mechanistic study†
Abstract
Reaction of (MePPh2)4WCl2 with C3O2 has been shown experimentally to result in stepwise cleavage of the two C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bonds in C3O2 to give successively tungsten complexes containing phosphinoketenylidene and phosphinocarbyne ligands. The mechanism of such processes has been elucidated by density functional theory methods for the L4WCl2 (L = PMe3, PMePh2) systems. The triplet L4WCl2 reagents are found to proceed to singlet intermediates and products in a reaction sequence involving dissociation of a phosphine ligand, a triplet → singlet intersystem crossing, an initial C
C double bonds in C3O2 to give successively tungsten complexes containing phosphinoketenylidene and phosphinocarbyne ligands. The mechanism of such processes has been elucidated by density functional theory methods for the L4WCl2 (L = PMe3, PMePh2) systems. The triplet L4WCl2 reagents are found to proceed to singlet intermediates and products in a reaction sequence involving dissociation of a phosphine ligand, a triplet → singlet intersystem crossing, an initial C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond cleavage and a free phosphine attachment transition state. The first step is the rate-determining step with a Gibbs free energy barrier of 19.8 kcal mol−1, and the formation of the stable phosphinoketenylidene intermediate is thermodynamically favorable. Further reaction of the phosphinoketenylidene intermediate to give the final phosphinocarbyne product is unusual because it is thermodynamically disfavored but kinetically feasible. The key steps involve loss of another phosphine ligand to give the transition state involving the cleavage of the second C
C bond cleavage and a free phosphine attachment transition state. The first step is the rate-determining step with a Gibbs free energy barrier of 19.8 kcal mol−1, and the formation of the stable phosphinoketenylidene intermediate is thermodynamically favorable. Further reaction of the phosphinoketenylidene intermediate to give the final phosphinocarbyne product is unusual because it is thermodynamically disfavored but kinetically feasible. The key steps involve loss of another phosphine ligand to give the transition state involving the cleavage of the second C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond of C3O2.
C bond of C3O2.
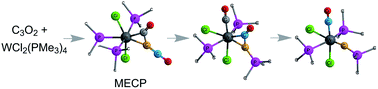

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...