Removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution using long TiO2 nanotubes with a high specific surface area†
Abstract
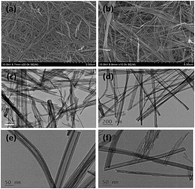
Long TiO2 nanotubes (TNs) were successfully prepared by the reaction of TiO2 and NaOH. The raw materials were treated by stirring, ion exchange, centrifugation, and freeze-drying, and then the target TNs was synthesized. Anatase TNs were obtained by calcinating the TNs at 823 K for 4.5 h. The TNs were characterized by Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectrometry. The results indicated that the TNs had a larger specific surface area (ca. 160 m2 g−1) and pore volume (ca. 0.6 cm3 g−1) than the commercial product P25. The adsorption of ciprofloxacin onto the TNs was compared with their adsorption onto P25. The adsorption isotherm, kinetics, and regeneration performance were investigated. The experimental results indicated that the maximum adsorption capacity of the TNs and P25 was 26.38 and 5.32 mg g−1, respectively, and their adsorption behavior was better fitted by the Langmuir model than by the Freundlich model. The kinetic regression results showed that the adsorption kinetics were more accurately represented by a pseudo-second-order model than by a pseudo-first-order model; the rate of the pseudo-second-order reactions on P25 and the anatase TNs were 0.0442 and 0.27463 min−1, respectively. After adsorption, the TNs had better regeneration properties than P25 under UV irradiation at 500 W for 3 h in 5 mL of aqueous solution. These results show that long TNs have a better adsorption capacity and regeneration properties than P25. This study provides a green method for the removal of organic pollutants by combining enrichment by adsorption with photocatalytic degradation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...