Torularhodin, isolated from Sporidiobolus pararoseus, inhibits human prostate cancer LNCaP and PC-3 cell growth through Bcl-2/Bax mediated apoptosis and AR down-regulation†
Abstract
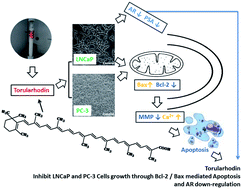
Torularhodin is one of the principal carotenoids in Sporidiobolus pararoseus and has a similar structure to that of lycopene. The present work was to elucidate its anti-cancer activity on androgen-dependent prostate cancer LNCaP cells and androgen-independent PC-3 cells using lycopene as a control. WST-1 assay showed that the efficiency of torularhodin was much better than lycopene on both prostate cell lines. Flow cytometry results demonstrated that its apoptotic induction was associated with loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased intracellular calcium concentration. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot data revealed that torularhodin changed the expression ratio of pro-apoptotic to anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members. Moreover, we found that torularhodin significantly down-regulated the expression levels of androgen receptor (AR) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) expression in LNCaP cells. The present results indicate that torularhodin inhibited the growth of LNCaP and PC-3 cells via the mitochondria-mediated pathway and the down-regulation of AR expression.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...