Fed-batch saccharification and ethanol fermentation of Jerusalem artichoke stalks by an inulinase producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae MK01
Abstract
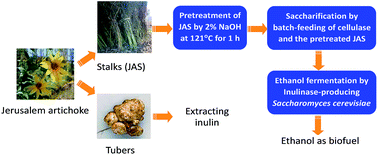
Jerusalem artichoke is a potential energy crop. While its tubers are being used to extract inulin, its stalks could be used for biofuels production. In this article, fed-batch saccharification and fermentation of Jerusalem artichoke stalks (JAS) was studied. Pretreatment with 2.0% (w/v) NaOH not only retained most inulin, the unique component in JAS, but also increased cellulose content from 42.3% to 58.2% due to the removal of lignin. Batch-feeding of both the pretreated JAS and cellulases was an effective strategy for saccharification, through which 115.8 g L−1 total sugars including glucose, xylose, fructose and inulin were released from 20% (w/v) solids uploading under the supplementation of cellulases at 20 FPU (filter paper unit) g−1 dry biomass. An inulinase-producing yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae MK01 was developed by the cell surface display of inulinase for ethanol fermentation from the pretreated JAS under the fed-batch conditions, and 38.3 g L−1 ethanol was produced at 96 h, with an ethanol yield of 0.361 g g−1 total sugars consumed, about 71% of the theoretical yield of 0.511, indicating that JAS would be a promising feedstock for ethanol production.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...