Electrochemical deposition of Fe2O3 in the presence of organic additives: a route to enhanced photoactivity†
Abstract
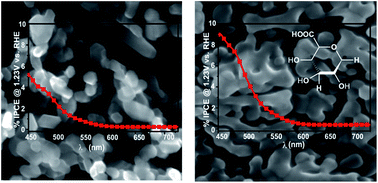
The photoelectrochemical activity of hematite films prepared by electrochemical deposition (ED) in the presence of organic additives is discussed. The studies focus on the role of small organic additive molecules in the tuning of the morphology of the films and their influence on the photoelectrochemical oxidation of water. The organic additives, namely, coumarin 343 (C343), γ-glucuronic acid (GA) and sodium dodecyl sulfonate (Sds), possess functional moieties to interact with iron ions in the ED bath electrostatically or through metal–ligand complexation reactions. XPS measurements prove that the organic additives are incorporated, and the oxidation state of Fe3+ rules out the presence of mixed valences in the films. SEM and XRD measurements present morphological and structural evidence, respectively. The photoelectrochemical study shows that organically modified hematite films exhibit enhanced photoactivity; the photocurrent density at 1.4 V vs. RHE on a GA-modified electrode is up to 5–6 times higher than on the unmodified electrode. Electrochemical impedance results reveal the role of the organic additives in reducing the charge transfer resistance from the hematite surface to the solution. In addition, a simple Ti post treatment greatly enhances the photoactivity of all electrodes under investigation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...