Micron-scale rod-like scattering particles for light trapping in nanostructured thin film solar cells†
Abstract
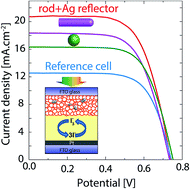
Spherical dielectric particles, nanofibers, and nanorods have been widely used as embedded scattering objects in nanostructured thin film solar cells. Here we propose micron-scale rod-like dielectric particles as a more effective alternative to the spherical ones for light trapping in thin film solar cells. The superior performance of these micro-rods is attributed to their larger scattering efficiency relative to the spherical particles as evidenced by full-wave optical calculations. Using a one-pot process, 1.7 μm-long bullet-shaped silica rods with 330 nm diameter are synthesized and their concentration in a N719-sensitized solar cell is optimized. A solar cell with an optimal concentration of rod-like particles delivers 8.74% power conversion efficiency (PCE), given the 6.33% PCE of the cell without any scattering particle. Moreover, a silver layer is deposited by chemical reduction of AgNO3 (Tollens' process) on the rear-side of the counter electrode, and hence the PCE of the optimal cell reaches 9.94%, showing 14% extra improvement due to the presence of the silver back-reflector. The rod-like scattering particles introduced here can be applied to other sensitized solar cells such as quantum-dot and organometallic perovskite solar cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...