Quercetin delivery to porcine cornea and sclera by solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsion†
Abstract
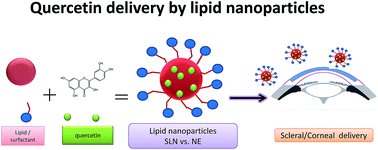
Quercetin is a flavonoid with strong antioxidant capacities. Recent studies indicate that quercetin can protect eye cells from oxidative damage. Lipid nanocarriers can protect the lipophilic drugs, achieving greater physical and chemical stability and controlling the release. Two potential nanocarriers including nanoemulsions (NE) and solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) are chosen as vehicles for quercetin encapsulation. Biocompatible surfactants Tween and Span were combined to develop oil in water interfaces to stabilize the quercetin. The size distribution of lipid nanocarriers was around 150–345 nm by using dynamic light scattering or transmission electron microscopy. The ocular quercetin delivery was confirmed by using confocal microscopy and ex vivo porcine eyes. The quercetin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles had the highest flux of 158 μg cm−2 on cornea after 24 hours. In addition, SLNs had the lowest cytotoxicity for cornea and retinal ganglion cells, and the value of half maximal inhibitory concentration were 268.85 and 211.3 μg ml−1, respectively. Quercetin loaded SLNs could efficiently protect cornea and retinal ganglion cells from H2O2-induced oxidative damages. Taken together, our results help to shed light on the complex interplay between the quercetin, the carrier composition, the ocular tissues and the antioxidant activities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...