New bifunctional-pullulan-based micelles with good biocompatibility for efficient co-delivery of cancer-suppressing p53 gene and doxorubicin to cancer cells
Abstract
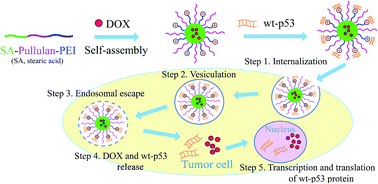
Combined treatment of drugs and therapeutic genes has emerged as a new modality of anticancer therapy. In this study, a new amphiphilic bifunctional pullulan derivative (named as PSP) containing stearic acid and low-molecular weight (1 kDa) branched polyethylenimine was prepared and evaluated as a nano-carrier for the co-delivery of a drug and gene for potential cancer therapy. The amphiphilic PSP could self-assemble into cationic core–shell nano-micelles in water, with a critical micelle concentration of around 58.9 mg L−1. PSP nanomicelles had an average size of 188.75 ± 3.18 nm, and a positive zeta potential of 17.83 ± 0.75 mV. The drug loading content and encapsulation efficiency of the PSP nanomicelles for doxorubicin (DOX), an anti-tumor drug, were about 5.10% and 56.07%, respectively, and DOX in PSP nanomicelles showed sustained release. The flow cytometry and confocal laser scanning microscopy showed that PSP/DOX nanomicelles could be successfully internalized by MCF-7 cells. The in vitro IC50 of PSP/DOX nanomicelles was slightly lower than that of free DOX against MCF-7 cells. Additionally, PSP nanomicelles condensed DNA efficiently to form compact structures, and induced comparable GFP gene expression level to Lipo2000 at N/P = 10 in gene transfection studies. In comparison with single DOX or p53 delivery, the co-delivery of DOX and therapy gene p53 using PSP micelles displayed higher cytotoxicity and induced a higher apoptosis rate of tumor cells in vitro. Moreover, PSP exhibited good blood compatibility and low cytotoxicity in the hemolysis and MTT assays, respectively. Altogether, PSP nanomicelles have a great potential in delivering hydrophobic anticancer drugs and therapeutic genes simultaneously for improved cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...