Comparison study of biosorption and coagulation/air flotation methods for chromium removal from wastewater: experiments and neural network modeling
Abstract
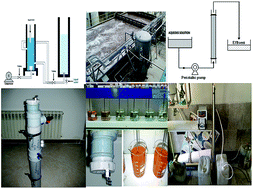
This work aims to compare a biosorption method (BM) and a coagulation–dissolved air flotation method (C/DAFM) as inexpensive and effective means of eliminating hexavalent chromium (Cr[VI]) from industrial wastewater. Synthetic wastewater containing 1000 mg L−1 chromium was used for the experiments. The effect of different parameters (initial pH, amount of adsorbent, and contact time) was investigated for the BM. At optimal conditions (initial pH 3, 7 g adsorbent, and contact time 120 min) maximum Cr(VI) removal was estimated to reach 68.1%. For the C/DAFM, poly aluminum chloride (PAC), and FeCl3 were used as coagulants and the dose was determined by jar test. In optimal conditions of pH 7.5, pressure of 3 bars, and flotation time of 5 min, a maximum of 85% of chromium was extracted. In a comparison of C/DAFM and BM, C/DAFM showed higher ability and greater potential for Cr(VI) removal. Process optimization was carried out using an artificial neural network (ANN) to predict the most favorable conditions of operation for maximum percentage of Cr(VI) removal from wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...