Manganese dioxide nanoparticles incorporated within ionic liquid derived fibrillated mesoporous carbon: electrode material for high-performance supercapacitors†
Abstract
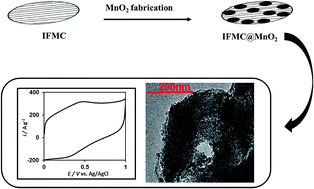
This article is the first example of the incorporation of metal oxide nanoparticles within ionic liquid derived nano-fibrillated mesoporous carbon (IFMC), as electrode materials for supercapacitor applications. Electron microscopy observations and X-ray diffraction analysis, in addition to gas adsorption/desorption analysis, confirm the incorporation of manganese dioxide within the mesoporous nanofibers (MnO2@IFMC) with a high surface area of about 388 m2 g−1. MnO2@IFMC was successfully employed as a new electrode material for high-rate supercapacitors in neutral media. The one-dimensional nano-composite shows high performance and excellent life cycle stability according to electrochemical studies. This substantial performance and high specific capacitance may originate from the high surface area of the nano-composite, shortened diffusion length and mesoporous openings on the outer surface. Also, augmented conductance of the carbon nanofibers due to the heteroatom (nitrogen) effect can be considered as an important reason for the high-rate capability and excellent specific capacitance (almost 1000 F g−1 at 10 mV s−1). Our results indicate that MnO2@IFMC can be considered as a promising electrode material for high-rate supercapacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...