Improvement in the performance of a zinc ion-selective potentiometric sensor using modified core/shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles
Abstract
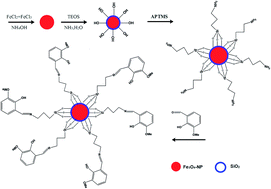
A novel, simple, accurate and sensitive zinc ion-selective potentiometric sensor was fabricated by modifying the surface of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles using a ligand (L) prepared by a coupled reaction between (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilan (APTMS) and 2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (2-H-3-MBA). The prepared Fe3O4 nanoparticles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). In addition, Fe3O4@SiO2, Fe3O4@SiO2–APTMS, and Fe3O4@SiO2–L were characterized by FTIR. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was used to confirm the surface modification of the Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles. The effects of individual variables such as the amount of graphite powder, Fe3O4@SiO2–L and sodium tetraphenylborate (NaTPB) used in the composition of the carbon paste electrode (CPE) in addition to their possible interactions were investigated and optimized using a central composite design (CCD) under response surface methodology (RSM). The optimal values of graphite powder, Fe3O4@SiO2–L and NaTPB in a proper amount of paraffin oil obtained were 72, 15 and 6 mg, respectively. The prepared electrode applied for sensing Zn2+ ions demonstrated a linear range of 2.5 × 10−6 to 1.00 × 10−1 mol L−1. The detection limit, slope and response time of this sensor were found to be 10−6 mol L−1, 29.451 and 14 s, respectively. The potentiometric response of the prepared electrode based on Fe3O4@SiO2–L was independent of the pH of the test solution over the pH range of 4–6, which is an advantage of this electrode having a neutral working pH. This sensor was successfully used for the sensitive determination of trace amounts of Zn2+ in samples of water. The moderate selectivity coefficient evaluated by the fixed interference method (FIM) indicated an efficient discriminating ability of the proposed electrode for Zn2+ ion assessment. It was also found to be well repeatable and reproducible.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...