Tea waste-supported hydrated manganese dioxide (HMO) for enhanced removal of typical toxic metal ions from water†
Abstract
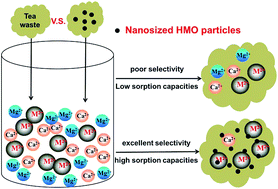
Tea waste (TW) was modified by depositing hydrated manganese oxide (HMO) onto it through in situ precipitation and a novel hybrid bio-adsorbent, namely HMO-TW, was obtained. The successful deposition of HMO in/on tea waste was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis. The removal of four typical heavy metals (i.e., Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Zn(II)) by HMO-TW was pH-dependent, and higher pH favored the sorption at the tested pHs of 2–7. HMO-TW showed excellent sorption selectivity toward all four metal ions, and the removal efficiency of target metal ions was sustained at 30%–90% even in the presence of 50 times higher competing Ca(II) and Mg(II) ions. Sorption isotherms of four metal ions by HMO-TW are all well represented by the Freundlich model, and the maximum experimental sorption capacities of Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) were 174.3, 78.38, 54.38 and 37.5 mg g−1, respectively. Compared to the unmodified tea waste, the sorption capacities and selectivity of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) onto HMO-TW improved significantly. The sorption process reached equilibrium within 200 min, and the kinetics could be well fitted by a pseudo-second order model. Fixed-bed column sorption results further showed that the bed volume (BV) of Ce/C0 reaching 0.5 for Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) were 1170, 1130, 820 and 1450 BV, respectively. In addition, the exhausted HMO-TW can be effectively regenerated using a 0.5 M HCl solution. All results reported herein validate that HMO-TW is a promising sorbent for practical treatment of heavy metal contaminated water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...