Nanoporous iron oxide@carbon composites with low carbon content as high-performance anodes for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
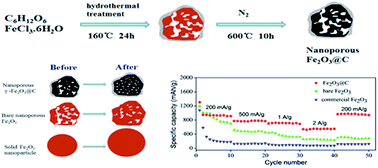
A composite of nanoporous iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles coated with a thin layer of carbon (designated as nanoporous Fe2O3@C) is synthesized using a convenient one-pot solvothermal method. Although the thickness of the carbon framework is only 6 nm on average, which is very small compared to the size of Fe2O3 nanoparticles, the carbon framework significantly enhances the electrochemical performance of nanoporous Fe2O3@C composites when they are used as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Thanks partly to the relatively low carbon content of 6.7 wt%, the nanoporous Fe2O3@C anodes exhibit a high reversible capacity of 767 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles at a current density of 500 mA g−1 and 545 mA h g−1 even at a higher current density of 2 A g−1. In comparison to commercial Fe2O3 nanoparticles and bare nanoporous Fe2O3 nanoparticles, the nanoporous Fe2O3@C anodes show superior cycle life. The nanoporous structure offers void space for volume change of Fe2O3 nanoparticles, while the thin carbon framework improves the stability of structures and SEI (solid electrolyte interphase) films during the continuous intercalation/deintercalation processes of Li ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...