Magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fiber capable of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride adsorption/separation in aqueous solution†
Abstract
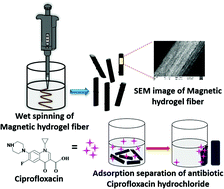
This work reports the successful preparation of magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers using a simple laboratory micropipette, employing the basic principle of the wet spinning technique without using any sophisticated instruments. The magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles used in this study were synthesized using a conventional co-precipitation method. The systematic characterisation of the magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers was done using FT-IR spectroscopy, XRD and SEM. The prepared magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers showed ferromagnetic behaviour when studied with the help of a vibrating sample magnetometer and can be easily separated using a strong magnet. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and tensile strength measurements reported an improvement in the thermostability and mechanical properties of the prepared magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers when compared to the blank alginate hydrogel fibers. All of these property enhancements in the alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers are suggestive of good compatibility and effective interactions between the alginate polymer matrix and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Also, the magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers were interestingly found to be very effective in the adsorption of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, while the blank alginate hydrogel fiber did not show any significant adsorption. Therefore, such magnetic alginate–Fe3O4 hydrogel fibers can work as a simple and cost-effective probe for the successful adsorption/separation of antibiotics, with the additional advantages of being easy to fabricate and having high thermal stability and mechanical strength.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...