Effect of chemically reduced graphene oxide on the isothermal and non-isothermal phase separation behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate)/poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) binary polymer blends
Abstract
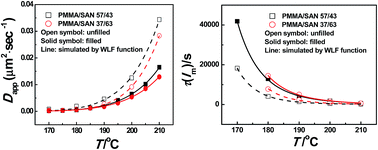
The effect of a small amount of chemically reduced graphene oxide (CRGO) on the isothermal and non-isothermal phase separation behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate)/poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) (PMMA/SAN) blends was investigated by using time-resolved small angle laser light scattering (SALLS). During the non-isothermal process, a quantitative logarithm function can be established to describe the relationship between the cloud point Tc and heating rate k as given by Tc = A ln k + T0 for the unfilled and filled CRGO-filled PMMA/SAN systems. During the isothermal process, the TTS principle and WLF function are applicable to describe the temperature dependence of nonlinear phase separation behaviors at the early and late stages of spinodal decomposition (SD) for such unfilled and filled systems, indicating that the introduction of CRGO hardly changes the viscous diffusion essence of macromolecular chains during phase separation. However, the mechanical barrier effect of CRGO on the macromolecular viscous diffusion may result in the delay of their phase separation behavior. Furthermore, the effect of CRGO on the isothermal and non-isothermal phase-separation behavior of the blend matrix is found to be dependent on the composition of the blend matrix. CRGO may act as a nucleating agent to result in the decrease of Tc for the PMMA/SAN 37/63 system, while the mechanical barrier effect of CRGO on the macromolecular segment may retard the concentration fluctuation at the early stage of SD phase separation to cause the increase of Tc for the PMMA/SAN 57/43 system. Besides, when SAN is the minority of the blend matrix (PMMA/SAN 57/43), the selective location of CRGO may result in the more obvious viscosity increment and then the more remarkable hindering effect on the SD phase separation behavior of blend matrix.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...