Flame retardant and toughening mechanisms of core–shell microspheres
Abstract
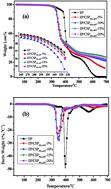
Epoxy (EP) composites containing polystyrene-ammonium polyphosphate core–shell microspheres (CSPPS-APP) were developed for flame retardant and toughening effects. The flame retardancy and thermal degradation behavior of the EP composites was investigated by limited oxygen index (LOI), vertical burning test (UL-94), cone calorimeter (CONE) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy capability (SEM-EDS) was used to characterize the morphology and elements of the residual chars. A possible flame retardant mechanism of the CSPPS-APP in EP matrix was proposed based on the CONE, TGA and SEM-EDS results. The influence of CSPPS-APP content on the glass transition temperature (Tg), storage modulus, Young's modulus, tensile strength and fracture toughness (KIC) of the material was also investigated. The results show that the CSPPS-APP microspheres lead to significant flame retardant and char formation effects on the EP. The Young's modulus and fracture toughness of the EP/CSPPS-APP composites increase with increasing CSPPS-APP content. The fracture toughness of the composite containing 15% CSPPS-APP increased by approximately 59% compared to that of the neat matrix. In addition, the critical strain energy release rate (GIC) of the epoxy increased from 159 to 409 J m−2 with the addition of 15% CSPPS-APP. The SEM images of the fracture surface indicate that the enhanced toughness of EP/CSPPS-APP composites can be attributed to the debonding of the core–shell microspheres and the subsequent plastic void growth of the matrix, as well as the crack deflection effect of CSPPS-APP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...