An experimental study on the stability of PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactors for CO2 absorption with alkanolamine solutions
Abstract
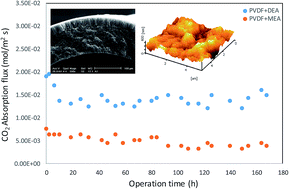
A previously developed PVDF hollow fiber membrane was prepared and its stability during CO2 absorption with alkanolamine solutions was investigated. The membrane was used in a gas–liquid membrane contactor module for over 160 h in a continuous operation using monoethanolamine (MEA) and diethanolamine (DEA) solutions (1 M) as the liquid absorbents. Before and after the CO2 absorption tests, the structures of the membranes were investigated in terms of morphology, N2 permeability, wetting resistance and mass transfer resistance, and thermal and mechanical stability. Under AFM and SEM analysis, the used membranes presented lower surface roughness, which was confirmed by outer surface contact angle measurement. From the CO2 absorption test, using MEA solution as the liquid absorbent, a gradual CO2 flux reduction of about 43% was observed until the end of the operation. The results of the permeation tests showed a decrease in the N2 permeance of the used membranes which was related to their smaller pore sizes due to changes in the surface properties. The mean membrane pore size was reduced from 15.8 nm to 6.8 and 2.24 nm for the membranes used with DEA and MEA solutions, respectively. The wetting resistance of the used membranes slightly decreased due to a reduction in surface hydrophobicity. Compared to the fresh membrane, the mass transfer resistance of the used membranes increased by about 16.8% and 20% when the DEA and MEA solutions were used, respectively. In addition, the used membranes showed lower mechanical stability in terms of elongation and tensile strength compared to the fresh membrane. The effect of the MEA solution on the surface properties of the membrane was greater than that of the DEA solution. It can be concluded that the stability of the PVDF membrane, in terms of its compatibility with the liquid absorbent, is a key factor which should be considered from an economic point of view.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...