Liposome collapse resulting from an allosteric interaction between 2,6-dimethyl-β-cyclodextrins and lipids†
Abstract
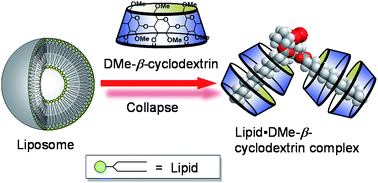
Although heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin (DMe-β-CDx) has been reported to exhibit higher cytotoxicity than many other cyclodextrins because of the way in which it abstracts cholesterols from liposomes, we have identified another reason for its cytotoxicity based on its interaction with lipids. These interactions exhibited nonlinear sigmoidal responses with Hill coefficient values (n) in the range of 3.0–3.6, which indicated that this phenomenon involves positive allosterism. Furthermore, analysis by mass spectroscopy revealed that the lipid–DMe-β-CDx complexes had stoichiometric ratios in the range of 1 : 1–1 : 4.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...