MALDI-TOF MS and ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry reveal specific porphyranase activity from a Pseudoalteromonas atlantica bacterial extract†
Abstract
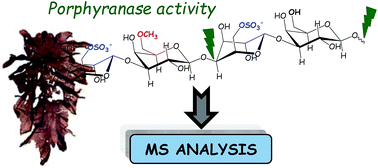
A better understanding of the chemical–physical properties of porphyran – a complex anionic polysaccharide – and the development of potential industrial applications requires more in-depth knowledge of its structural organization. The structural complexity of the hybrid (co-polymer) structure of porphyran stems from the co-occurrence of two repetition moieties LA-G and L6S-G, which can be methylated on the D-galactose. The enzymes currently available for the structural analyses of porphyran are limited in specificity, and methylated porphyran cannot be digested by previously described β-porphyranases. Here, MALDI-TOF MS analysis and tandem ESI-MS sequencing of porphyran degradation products after incubation with protein extracts from the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas atlantica revealed methylated disaccharide (L6S-GMe) and dimethylated tetrasaccharide (L6S-GMe–L6S-GMe) end-products that have never been described before. Our results highlighted unprecedented β-methyl-porphyranase activity that can accommodate the methylated building blocks of porphyran.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...