Synthesis and characterization of pH-responsive nanohydrogels as biocompatible drug carriers based on chemically modified tragacanth gum polysaccharide
Abstract
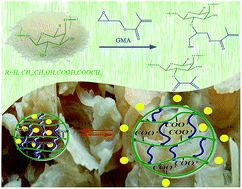
In this work, the preparation of pH-responsive nanohydrogels based on tragacanth gum (TG) polysaccharide and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was investigated. Ring opening of the epoxide group of GMA by hydroxyl groups of TG led to the preparation of TG–GMA which was then transformed to a cross-linked nanohydrogel network (TG-MA) via radical polymerization using K2S2O8 as an initiator. The obtained nanohydrogels were characterized using techniques such as FT-IR, 1H NMR, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), zeta sizer and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The gel content of the nanohydrogels showed dependence on the weight ratio of TG/GMA. According to the results, the swelling behavior of the prepared TG-MA nanohydrogels showed significant dependence on the gel content, pH, and immersion time. The loading and in vitro release of quercetin as a model drug was investigated at pH 7.0. The obtained results showed that the rate of drug release depends on the swelling of nanohydrogels and cross-linker content. Furthermore, the investigation shows that pH-responsive TG-MA nanohydrogels can be good candidates for further tests as drug carriers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...