CdS : SiO2 nanocomposite as a luminescence-based wide range temperature sensor
Abstract
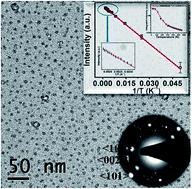
A wide range (20–560 K) temperature sensor is devised for the first time from CdS : SiO2 nanocomposite thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Highly intense, stable, and broad red emission observed from the CdS : SiO2 nanocomposite is employed to obtain a luminescence thermometer. Nearly monodisperse and small sized CdS nanocrystals (∼3 nm) in a SiO2 matrix, as viewed by transmission electron microscopy, may be accountable for the absence of band edge emission even at 20 K. The sensor exhibits almost linear behavior in all cryogenic, physiological, and high temperature ranges. The average sensitivity and resolution of the sensor reported here were ≈10−2 K−1 and 10−4 K, respectively, with a maximum relative sensitivity of ∼8.4% K−1 at 120 K.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...